Create a stored procedure where you can input a movie title or actor’s name you like,and it will return the top five suggestions based on either movies the actor has starred in or films with similar genres.
我的第一次尝试是正确但缓慢.返回结果可能需要2000毫秒.
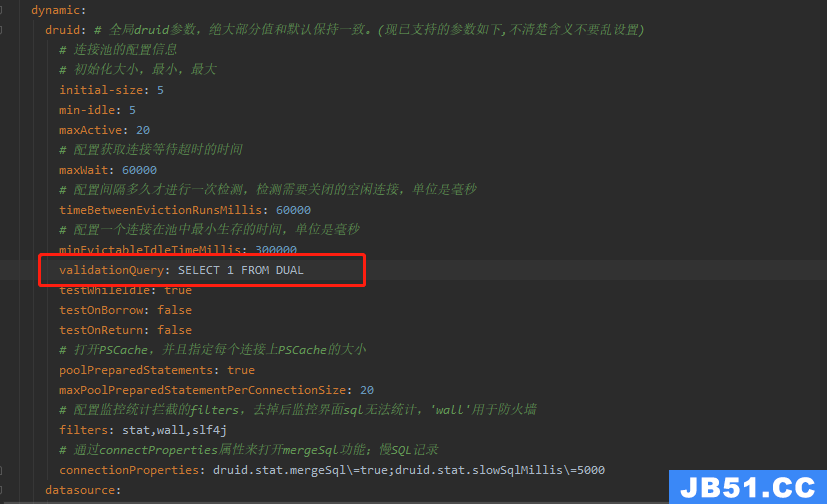
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION suggest_movies(IN query text,IN result_limit integer DEFAULT 5)
RETURNS TABLE(movie_id integer,title text) AS
$BODY$
WITH suggestions AS (
SELECT
actors.name AS entity_term,movies.movie_id AS suggestion_id,movies.title AS suggestion_title,1 AS rank
FROM actors
INNER JOIN movies_actors ON (actors.actor_id = movies_actors.actor_id)
INNER JOIN movies ON (movies.movie_id = movies_actors.movie_id)
UNION ALL
SELECT
searches.title AS entity_term,suggestions.movie_id AS suggestion_id,suggestions.title AS suggestion_title,RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY searches.movie_id ORDER BY cube_distance(searches.genre,suggestions.genre)) AS rank
FROM movies AS searches
INNER JOIN movies AS suggestions ON
(searches.movie_id <> suggestions.movie_id) AND
(cube_enlarge(searches.genre,2,18) @> suggestions.genre)
)
SELECT suggestion_id,suggestion_title
FROM suggestions
WHERE entity_term = query
ORDER BY rank,suggestion_id
LIMIT result_limit;
$BODY$
LANGUAGE sql;
我的第二次尝试是正确而快速的.我通过将过滤器从CTE推进到联合的每个部分来优化它.
我从外部查询中删除了这一行:
WHERE entity_term = query
我在第一个内部查询中添加了这一行:
WHERE actors.name = query
我将此行添加到第二个内部查询:
WHERE movies.title = query
第二个函数大约需要10毫秒才能返回相同的结果.
除了函数定义之外,数据库没有什么不同.
为什么PostgreSQL会为这两个逻辑上等效的查询生成这样的不同计划?
第一个函数的EXPLAIN ANALYZE计划如下所示:
Limit (cost=7774.18..7774.19 rows=5 width=44) (actual time=1738.566..1738.567 rows=5 loops=1)
CTE suggestions
-> Append (cost=332.56..7337.19 rows=19350 width=285) (actual time=7.113..1577.823 rows=383024 loops=1)
-> Subquery Scan on "*SELECT* 1" (cost=332.56..996.80 rows=11168 width=33) (actual time=7.113..22.258 rows=11168 loops=1)
-> Hash Join (cost=332.56..885.12 rows=11168 width=33) (actual time=7.110..19.850 rows=11168 loops=1)
Hash Cond: (movies_actors.movie_id = movies.movie_id)
-> Hash Join (cost=143.19..514.27 rows=11168 width=18) (actual time=4.326..11.938 rows=11168 loops=1)
Hash Cond: (movies_actors.actor_id = actors.actor_id)
-> Seq Scan on movies_actors (cost=0.00..161.68 rows=11168 width=8) (actual time=0.013..1.648 rows=11168 loops=1)
-> Hash (cost=80.86..80.86 rows=4986 width=18) (actual time=4.296..4.296 rows=4986 loops=1)
Buckets: 1024 Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 252kB
-> Seq Scan on actors (cost=0.00..80.86 rows=4986 width=18) (actual time=0.009..1.681 rows=4986 loops=1)
-> Hash (cost=153.61..153.61 rows=2861 width=19) (actual time=2.768..2.768 rows=2861 loops=1)
Buckets: 1024 Batches: 1 Memory Usage: 146kB
-> Seq Scan on movies (cost=0.00..153.61 rows=2861 width=19) (actual time=0.003..1.197 rows=2861 loops=1)
-> Subquery Scan on "*SELECT* 2" (cost=6074.48..6340.40 rows=8182 width=630) (actual time=1231.324..1528.188 rows=371856 loops=1)
-> WindowAgg (cost=6074.48..6258.58 rows=8182 width=630) (actual time=1231.324..1492.106 rows=371856 loops=1)
-> Sort (cost=6074.48..6094.94 rows=8182 width=630) (actual time=1231.307..1282.550 rows=371856 loops=1)
Sort Key: searches.movie_id,(cube_distance(searches.genre,suggestions_1.genre))
Sort Method: external sort Disk: 21584kB
-> Nested Loop (cost=0.27..3246.72 rows=8182 width=630) (actual time=0.047..909.096 rows=371856 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on movies searches (cost=0.00..153.61 rows=2861 width=315) (actual time=0.003..0.676 rows=2861 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using movies_genres_cube on movies suggestions_1 (cost=0.27..1.05 rows=3 width=315) (actual time=0.016..0.277 rows=130 loops=2861)
Index Cond: (cube_enlarge(searches.genre,2::double precision,18) @> genre)
Filter: (searches.movie_id <> movie_id)
Rows Removed by Filter: 1
-> Sort (cost=436.99..437.23 rows=97 width=44) (actual time=1738.565..1738.566 rows=5 loops=1)
Sort Key: suggestions.rank,suggestions.suggestion_id
Sort Method: top-N heapsort Memory: 25kB
-> CTE Scan on suggestions (cost=0.00..435.38 rows=97 width=44) (actual time=1281.905..1738.531 rows=43 loops=1)
Filter: (entity_term = 'Die Hard'::text)
Rows Removed by Filter: 382981
Total runtime: 1746.623 ms
第二个查询的EXPLAIN ANALYZE计划如下所示:
Limit (cost=43.74..43.76 rows=5 width=44) (actual time=1.231..1.234 rows=5 loops=1)
CTE suggestions
-> Append (cost=4.86..43.58 rows=5 width=391) (actual time=1.029..1.141 rows=43 loops=1)
-> Subquery Scan on "*SELECT* 1" (cost=4.86..20.18 rows=2 width=33) (actual time=0.047..0.047 rows=0 loops=1)
-> Nested Loop (cost=4.86..20.16 rows=2 width=33) (actual time=0.047..0.047 rows=0 loops=1)
-> Nested Loop (cost=4.58..19.45 rows=2 width=18) (actual time=0.045..0.045 rows=0 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using actors_name on actors (cost=0.28..8.30 rows=1 width=18) (actual time=0.045..0.045 rows=0 loops=1)
Index Cond: (name = 'Die Hard'::text)
-> Bitmap Heap Scan on movies_actors (cost=4.30..11.13 rows=2 width=8) (never executed)
Recheck Cond: (actor_id = actors.actor_id)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on movies_actors_actor_id (cost=0.00..4.30 rows=2 width=0) (never executed)
Index Cond: (actor_id = actors.actor_id)
-> Index Scan using movies_pkey on movies (cost=0.28..0.35 rows=1 width=19) (never executed)
Index Cond: (movie_id = movies_actors.movie_id)
-> Subquery Scan on "*SELECT* 2" (cost=23.31..23.40 rows=3 width=630) (actual time=0.982..1.081 rows=43 loops=1)
-> WindowAgg (cost=23.31..23.37 rows=3 width=630) (actual time=0.982..1.064 rows=43 loops=1)
-> Sort (cost=23.31..23.31 rows=3 width=630) (actual time=0.963..0.971 rows=43 loops=1)
Sort Key: searches.movie_id,suggestions_1.genre))
Sort Method: quicksort Memory: 28kB
-> Nested Loop (cost=4.58..23.28 rows=3 width=630) (actual time=0.808..0.916 rows=43 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using movies_title on movies searches (cost=0.28..8.30 rows=1 width=315) (actual time=0.025..0.027 rows=1 loops=1)
Index Cond: (title = 'Die Hard'::text)
-> Bitmap Heap Scan on movies suggestions_1 (cost=4.30..14.95 rows=3 width=315) (actual time=0.775..0.844 rows=43 loops=1)
Recheck Cond: (cube_enlarge(searches.genre,18) @> genre)
Filter: (searches.movie_id <> movie_id)
Rows Removed by Filter: 1
-> Bitmap Index Scan on movies_genres_cube (cost=0.00..4.29 rows=3 width=0) (actual time=0.750..0.750 rows=44 loops=1)
Index Cond: (cube_enlarge(searches.genre,18) @> genre)
-> Sort (cost=0.16..0.17 rows=5 width=44) (actual time=1.230..1.231 rows=5 loops=1)
Sort Key: suggestions.rank,suggestions.suggestion_id
Sort Method: top-N heapsort Memory: 25kB
-> CTE Scan on suggestions (cost=0.00..0.10 rows=5 width=44) (actual time=1.034..1.187 rows=43 loops=1)
Total runtime: 1.410 ms
PostgreSQL 9.3不为CTE做predicate pushdown.
执行谓词下推的优化器可以将where子句移动到内部查询中.目标是尽早过滤掉不相关的数据.只要新查询在逻辑上等效,引擎仍然会获取所有相关数据,因此只能更快地生成正确的结果.
核心开发人员Tom Lane暗示难以确定pgsql-performance mailing list的逻辑等价.
CTEs are also treated as optimization fences; this is not so much an
optimizer limitation as to keep the semantics sane when the CTE contains
a writable query.
优化器不区分只读CTE和可写CTE,因此在考虑计划时过于保守. ‘fence’处理阻止优化器移动CTE中的where子句,尽管我们可以看到它是安全的.
我们可以等待PostgreSQL团队改进CTE优化,但是为了获得良好的性能,你必须改变你的写作风格.
重写性能
这个问题已经显示了一种获得更好计划的方法.复制过滤条件基本上是硬编码谓词下推的效果.
在这两个计划中,引擎将结果行复制到工作表,以便对它们进行排序.工作表越大,查询越慢.
第一个计划将基表中的所有行复制到工作表,并扫描它以查找结果.为了使事情变得更慢,引擎必须扫描整个工作表,因为它没有索引.
这是一项荒谬的不必要工作.当基表中估计的19350行中只有估计的5个匹配行时,它会两次读取基表中的所有数据以找到答案.
第二个计划使用索引来查找匹配的行,并将这些行复制到工作表中.该索引为我们有效地过滤了数据.
在The Art of SQL的page 85中,StéphaneFaroult提醒我们用户的期望.
To a very large extent,end users adjust thier patience to the number of rows they expect: when they ask for one needle,they pay little attention to the size of the haystack.
第二个计划与针一起扩展,因此更有可能让您的用户满意.
重写可维护性
新查询难以维护,因为您可以通过更改一个过滤器epxression而不是另一个过滤器epxression来引入缺陷.
如果我们只能写一次并且仍能获得良好的表现,那不是很好吗?
我们可以.优化器对子查询进行谓词下推.
一个更简单的例子更容易解释.
CREATE TABLE a (c INT); CREATE TABLE b (c INT); CREATE INDEX a_c ON a(c); CREATE INDEX b_c ON b(c); INSERT INTO a SELECT 1 FROM generate_series(1,1000000); INSERT INTO b SELECT 2 FROM a; INSERT INTO a SELECT 3;
这将创建两个表,每个表都有一个索引列.他们一起包含一百万个,一百万个,一个三个.
您可以使用以下任一查询找到针3.
-- CTE EXPLAIN ANALYZE WITH cte AS ( SELECT c FROM a UNION ALL SELECT c FROM b ) SELECT c FROM cte WHERE c = 3; -- Subquery EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT c FROM ( SELECT c FROM a UNION ALL SELECT c FROM b ) AS subquery WHERE c = 3;
CTE的计划很慢.引擎扫描三个表并读取大约四百万行.它需要近1000毫秒.
CTE Scan on cte (cost=33275.00..78275.00 rows=10000 width=4) (actual time=471.412..943.225 rows=1 loops=1)
Filter: (c = 3)
Rows Removed by Filter: 2000000
CTE cte
-> Append (cost=0.00..33275.00 rows=2000000 width=4) (actual time=0.011..409.573 rows=2000001 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on a (cost=0.00..14425.00 rows=1000000 width=4) (actual time=0.010..114.869 rows=1000001 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on b (cost=0.00..18850.00 rows=1000000 width=4) (actual time=5.530..104.674 rows=1000000 loops=1)
Total runtime: 948.594 ms
子查询的计划很快.引擎只是寻找每个指数.它需要不到一毫秒.
Append (cost=0.42..8.88 rows=2 width=4) (actual time=0.021..0.038 rows=1 loops=1)
-> Index Only Scan using a_c on a (cost=0.42..4.44 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.020..0.021 rows=1 loops=1)
Index Cond: (c = 3)
Heap Fetches: 1
-> Index Only Scan using b_c on b (cost=0.42..4.44 rows=1 width=4) (actual time=0.016..0.016 rows=0 loops=1)
Index Cond: (c = 3)
Heap Fetches: 0
Total runtime: 0.065 ms
有关交互式版本,请参阅SQLFiddle.
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。