注:这篇文章只是讲解React Redux这一层,并不包含Redux部分。Redux有计划去学习,等以后学习了Redux源码以后再做分析
注:代码基于现在(2016.12.29)React Redux的最新版本(5.0.1)
Utils篇
这一小节里面先把基础的Utils代码过一遍,以后看核心代码的时候方便一点。由于是Utils不涉及文档,所以没有文档方面的展示
shallowEqual.js
从名字中就能看出这个的作用,其实就只是做了一个浅比较,对象中的value直接用 === 来比较,所以如果遇到复杂的object进行比较,就会返回false。最基础的就是shallowEqual({a:{}},{a:{}}) === false
const hasOwn = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty
export default function shallowEqual(a,b) {
if (a === b) return true
let countA = 0
let countB = 0
for (let key in a) {
if (hasOwn.call(a,key) && a[key] !== b[key]) return false
countA++
}
for (let key in b) {
if (hasOwn.call(b,key)) countB++
}
return countA === countB
}
代码比较简单,基本思路就是:
对代码的一点疑问:
countA++之前,要不要检查一下是否是OwnProperty?我已经在segmentfault里面提了问题,LionKissDeer在github上发了issue,并得到回复,确实是一个问题。
用countA,countB来记录数量,而不是用Object.keys(a).length来进行对比,可以理解为减少操作和不必要的内存使用。那么是否只用一个countA,然后再第二个for...in中进行countA--,最后比较countA === 0更好?
storeShape.js
这个真的只是store的shape,不需要解释
import { PropTypes } from 'react'
export default PropTypes.shape({
subscribe: PropTypes.func.isrequired,dispatch: PropTypes.func.isrequired,getState: PropTypes.func.isrequired
})
warning.js
简单的一个报错的方法,主要是检查了console是否存在的情况。中间有提到一点,如果console打开了'break on all exception'选项,那么就会在这个warning的地方停下
/** * Prints a warning in the console if it exists. * * @param {String} message The warning message. * @returns {void} */ export default function warning(message) { /* eslint-disable no-console */ if (typeof console !== 'undefined' && typeof console.error === 'function') { console.error(message) } /* eslint-enable no-console */ try { // This error was thrown as a convenience so that if you enable // "break on all exceptions" in your console,// it would pause the execution at this line. throw new Error(message) /* eslint-disable no-empty */ } catch (e) {} /* eslint-enable no-empty */ }
verifyPlainObject.js
通过判断是否是plainObject,使用lodash来判断,并给个warning。这个方法主要是用在非production环境下,对数据格式进行检测,并抛出异常
import isPlainObject from 'lodash/isPlainObject' import warning from './warning' export default function verifyPlainObject(value,displayName,methodName) { if (!isPlainObject(value)) { warning( `${methodName}() in ${displayName} must return a plain object. Instead received ${value}.` ) } }
wrapActionCreators.js
这里是通过这个方法生成一个(actionCreators)=>(dispatch)=>()=>binded actions的方法。bindActionCreators的作用是返回用dispatch绑定过的actions,具体方法可以在Redux文档中查看。
然而,我并没有在react-redux的代码里看到这个方法的调用,文档中也没有提到过这个方法,虽然在mapDispatchToProps.js中看到了一样的代码片段…不知道是不是老代码没有删除干净,还是新功能需要,但是还没有上线…
import { bindActionCreators } from 'redux'
export default function wrapActionCreators(actionCreators) {
return dispatch => bindActionCreators(actionCreators,dispatch)
}
Subscription.js
这里是用一个典型的订阅发布模式,通过对store或父级subscription进行监听,来进行组件的更新(onStateChange)。
createListenerCollection function
先放一个工厂模式的代码,这段主要是用来生成listener的工厂:
const CLEARED = null
const nullListeners = { notify() {} }
function createListenerCollection() {
// the current/next pattern is copied from redux's createStore code.
// Todo: refactor+expose that code to be reusable here?
let current = []
let next = []
return {
clear() {
next = CLEARED
current = CLEARED
},notify() {
const listeners = current = next
for (let i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
listeners[i]()
}
},subscribe(listener) {
let isSubscribed = true
if (next === current) next = current.slice()
next.push(listener)
return function unsubscribe() {
if (!isSubscribed || current === CLEARED) return
isSubscribed = false
if (next === current) next = current.slice()
next.splice(next.indexOf(listener),1)
}
}
}
}
这段很简单的实现了一个listener的工厂,包含notify,subscribe,unsubscribe和clear等订阅发布模式的基本功能。
值得注意的是,这里使用了current/next模式,这里主要是为了防止在notify中,listeners[i]()运行的时候对current对象作出内容删除操作,从而导致notify出错。
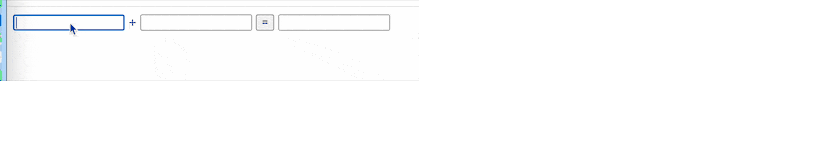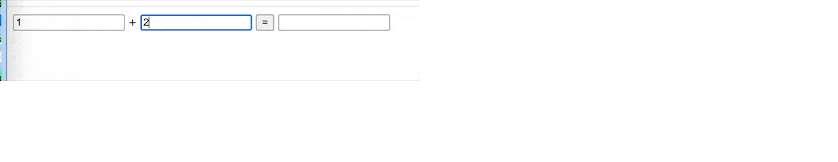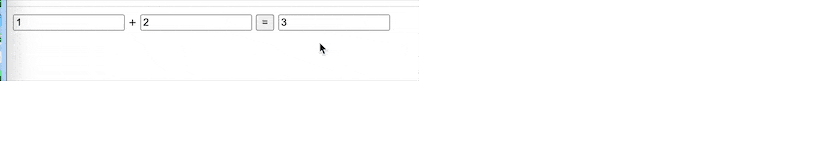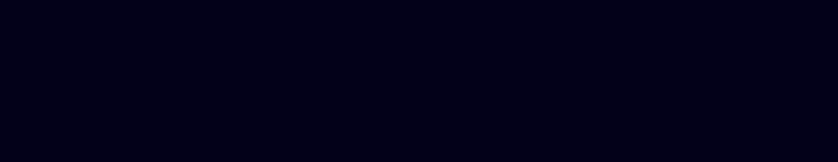
举个栗子,我们要运行下面这段代码:
var listener = createListenerCollection();
var helloUnsub = listener.subscribe(()=>{ console.log("Hello"); });
var worldUnsub = listener.subscribe(()=>{ console.log("world"); helloUnsub(); });
var unsub = listener.subscribe(()=>{ console.log("!!"); });
listener.notify(); // 期望输出的是Hello world !!
listener.notify(); // 期望输出的是world !!
然后我们用修改过没有用next/current模式的代码运行:
function createListenerCollection() {
let current = []
return {
notify() {
const listeners = current
for (let i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
listeners[i]()
}
},subscribe(listener) {
let isSubscribed = true
current.push(listener)
return function unsubscribe() {
if (!isSubscribed || current === CLEARED) return
isSubscribed = false
current.splice(current.indexOf(listener),1)
}
}
}
}
看一下输出结果:
发现第一次输出的时候,少输出了一次。
在这里,我们在world的输出后,取消hello的subscribe。这里就会造成:输出完world以后,删除了hello,代码里listeners.length的判断就自动减少了1,所以导致!!没有输出。
而如果使用next/current模式的话,由于我们对unsubscribe的操作都是对新的next进行操作,所以不会影响listeners,就不会出现上面的问题。
Subscription class
一个简单的封装:
export default class Subscription {
constructor(store,parentSub) {
this.store = store
this.parentSub = parentSub
this.unsubscribe = null
this.listeners = nullListeners
}
addnestedSub(listener) {
this.trySubscribe()
return this.listeners.subscribe(listener)
}
notifynestedSubs() {
this.listeners.notify()
}
isSubscribed() {
return Boolean(this.unsubscribe)
}
trySubscribe() {
if (!this.unsubscribe) {
// this.onStateChange is set by connectAdvanced.initSubscription()
this.unsubscribe = this.parentSub
? this.parentSub.addnestedSub(this.onStateChange)
: this.store.subscribe(this.onStateChange)
this.listeners = createListenerCollection()
}
}
tryUnsubscribe() {
if (this.unsubscribe) {
this.unsubscribe()
this.unsubscribe = null
this.listeners.clear()
this.listeners = nullListeners
}
}
}
唯一需要注意的一点是,他们的onStateChange事件其实是绑定在父级(parentSub)或者store的subscription上面的。至于为什么要绑定在父级或者store上面,是因为父级发生了改变,就会通知下级,下级再通知下下级…所以下级需要连接到上级上。
调用模式大概是这样子的,由上到下由顶层store一层一层到leaf:
不明白的一点:
这样子绑定上级的方法,和所有都直接绑定到store上面有什么不同?已提问
一点总结
shallowEqual的简单实现,感觉完全可以不用插件自己写一个,比较简单。在上面关于shallowEqual的github上面,React Redux的作者有提到建议使用fbjs的shallowEqual
next/current模式,特别适用于在循环中可能会对循环对象进行增删的情况,可以考虑使用这个模式。通过生成一个影对象,对影对象进行修改,需要循环的时候,再赋值给current对象
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。