1. C Regex
1.1. 前言
GUN C Library支持两种正则表达式的匹配接口,其一为标准的POSIX.2接口,其二为GUN C Library已经有的。两种接口都声明在regex.h中,如果#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE,将使用POSIX.2接口。
1.2. 编译正则表达式
这里的编译不是指生成一条机器指令,而是指生成一个特殊的结构体:regex_t。regex_t中保存有编译后的正则表达式,它实际上是一个结构体,其中通常使用到的成员变量是re_nsub,存放括号里的字表达式数目。
在定义regex_t后,我们就可以编译了:
int regcomp (regex_t *compiled,const char *restrict pattern,int cflags)complied : 为前面定义的regex_t变量地址
pattern : 为自定义的正则表达式
cflags : 指定正则表达式语法及语义的选项,其中选项主要如下:
REG_NOSUB : 使用此标志,regcomp将不保存子表达式的相关信息,如果不使用此标志,则compiled->re_nsub将记录子表达式数目。
REG_EXTENDED : 将pattern作为扩展的正则表达式,而不是basic正则表达式。
REG_ICASE : 匹配过程中忽略大小写
REG_NEWLINE:
返回值:
成功返回0,失败返回非0值,可通过regerror进行详细信息查看。
1.3. 匹配正则表达式
int regexec (const regex_t *compiled,const char *string,size_t nmatch,regmatch_t matchptr[restrict],int eflags)compiled :为编译后的regex_t变量
string :为待匹配的字符串
matchptr :存储匹配结果信息
eflags :位模式,主要选项如下:
REG_NOTBOL
Do not regard the beginning of the specified string as the beginning of a line; more generally,don't make any assumptions about what text might precede it.
REG_NOTEOL
Do not regard the end of the specified string as the end of a line; more generally,don't make any assumptions about what text might follow it.
返回值:
成功返回0,失败返回非0值,可通过regerror进行详细信息查看。
regmatch_t:存放匹配结果的偏移信息,主要包含两个成员变量:
rm_so :匹配成功的子串在原字符串中的起始偏移地址
rm_eo :匹配成功的子串在原字符串中的结束偏移地址
在传递的regmatch_t数组中,index 0保存匹配整个正则表达式的字符串信息,index i(i>0)则依次匹配第i个子表达式匹配信息。如果你不关心这些信息,可以设置nmatch为0,或者设置REG_NOSUB标志。
1.4. 释放
在再次使用regex_t进行其他正则表达式匹配前,必须释放regex_t结构体。void regfree (regex_t *compiled)获取执行错误信息
size_t regerror (int errcode,const regex_t *compiled,char *restrict buffer,size_t length)
char *get_regerror (int errcode,regex_t *compiled)
{
size_t length = regerror (errcode,compiled,NULL,0);
char *buffer = xmalloc (length);
(void) regerror (errcode,buffer,length);
return buffer;
}
1.5. 示例
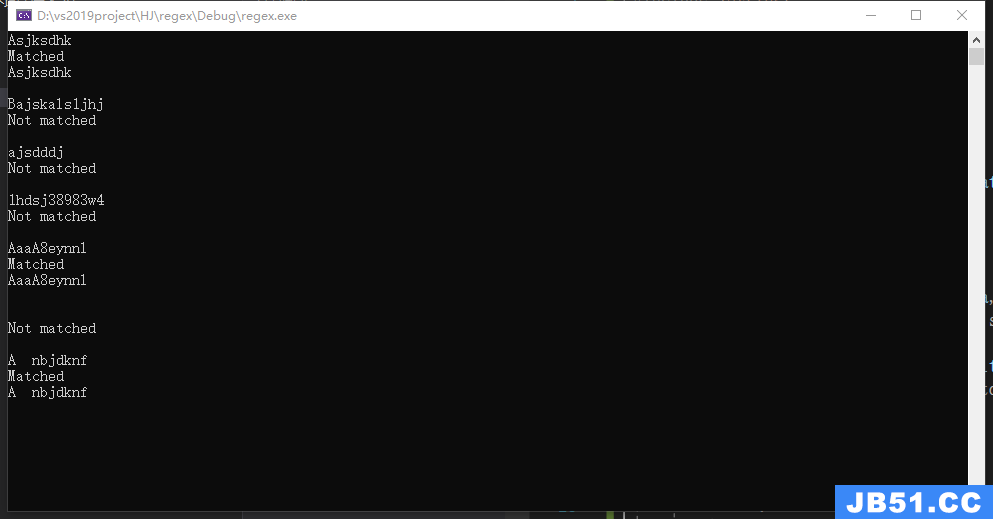
#include <sys/types.h> #include <regex.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> char* get_regerror(int errorcode,regex_t *complied) { size_t length = regerror(errorcode,complied,0); char *buffer = (char*)malloc(length); regerror(errorcode,length); return buffer; } int main(int argc,char **argv) { regex_t regex; const size_t nmatch = 1; regmatch_t pmatch[1]; const char pattern[] = "[[:digit:]]+"; char *buf = "12abc45"; int status; if(0 != (status = regcomp(®ex,pattern,REG_EXTENDED))){ printf("regcomp Failed:%s\n",get_regerror(status,®ex)); regfree(®ex); exit(1); } while(1){ status = regexec(®ex,buf,nmatch,pmatch,0); if(REG_NOMATCH == status){ printf("%s\n",®ex)); break; }else if(0 == status){ printf("Match:"); size_t length = pmatch[0].rm_eo - pmatch[0].rm_so; char *result = (char*)malloc(length+1); strncpy(result,buf+pmatch[0].rm_so,length); result[length]='\0'; printf("%s\n",result); free(result); buf += pmatch[0].rm_eo; }else{ printf("regexec Failed :%s\n",®ex)); break; } } regfree(®ex); return 0; }
2. boost Regex
2.1. 前言
The algorithms regex_search and regex_match make use of match_results to report what matched; the difference between these algorithms is that regex_match will only find matches that consume all of the input text,where as regex_search will search for a match anywhere within the text being matched.2.2. basic_regex
class basic_regex; typedef basic_regex<char> regex; typedef basic_regex<wchar_t> wregex;
其中,我们通常会用到以下几个功能:
bool empty() const;如果正则表达式非法则返回true,否则返回false。
size_type mark_count() const;返回正则表达式标记的子表达式数目
flag_type flags() const;返回一个位掩码,为构造basic_regex时传递的标志位。
int status() const;如果表达式有效则返回0。主要用于不能抛出异常的环境。
2.3. match_results
match_results主要用作参数传递给regex_match和regex_search,以及作为regex_iterator迭代器的返回值。class match_results; typedef match_results<const char*> cmatch; typedef match_results<const wchar_t*> wcmatch; typedef match_results<string::const_iterator> smatch; typedef match_results<wstring::const_iterator> wsmatch;
size_type size() const;返回保存在*this中sub_match数目,也是子表达式数目+1
bool empty()const;Returns size() == 0.
string_type str(int sub = 0)const; string_type str(constchar_type* sub)const;将子表达式作为string类型返回:sring_type((*this)[sub])
const_reference operator[](int n) const返回第n个sub_match的引用。如果n==0,则返回匹配整个正则表达式的sub_match,如果n越界或非法,则返回的sub_match的matched值为false
const_reference prefix()const;Effects: Returns a reference to the sub_match object representing the character sequence from the start of the string being matched or searched,to the start of the match found.
const_reference suffix()const;Effects: Returns a reference to the sub_match object representing the character sequence from the end of the match found to the end of the string being matched or searched.
const_iterator begin()const;
Effects: Returns a starting iterator that enumerates over all the marked sub-expression matches stored in *this.
const_iterator end()const;
Effects: Returns a terminating iterator that enumerates over all the marked sub-expression matches stored in *this.
2.4. sub_match
When the marked sub-expression denoted by an object of type sub_match participated in a regular expression match then member matched evaluates to true,and members first and second denote the range of characters [first,second) which formed that match. Otherwise matched is false,and members first and second contained undefined values.If an object of type sub_match represents sub-expression 0 - that is to say the whole match - then member matched is always true,unless a partial match was obtained as a result of the flag match_partial being passed to a regular expression algorithm,in which case member matched is false,and members first and second represent the character range that formed the partial match.
typedef BidirectionalIterator iterator;
The iterator type.
iterator first
An iterator denoting the position of the start of the match.
iterator second
An iterator denoting the position of the end of the match.
bool matched
A Boolean value denoting whether this sub-expression participated in the match.
static difference_type length();Effects: returns the length of this matched sub-expression,or 0 if this sub-expression was not matched: matched ? dis-tance(first,second) : 0).
basic_string<value_type> str()const;Effects: returns a string representation of *this: (matched ? basic_string<value_type>(first,second) : ba-sic_string<value_type>()).
2.5. regex_match
Note that the result is true only if the expression matches the whole of the input sequence. If you want to search for an expression somewhere within the sequence then use regex_search.template <classBidirectionalIterator,classcharT,classtraits> bool regex_match(BidirectionalIterator first,BidirectionalIterator last,constbasic_regex <charT,traits>& e,match_flag_typeflags= match_default); template <classcharT,classAllocator,classtraits> bool regex_match(constcharT* str,match_results<constcharT*,Allocator>& m,match_flag_typeflags= match_default);
2.6. regex_search
template<classcharT,classtraits> bool regex_search(constcharT* str,constbasic_regex<charT,match_flag_typeflags= match_default); template <classBidirectionalIterator,classtraits> bool regex_search(BidirectionalIterator first,match_flag_typeflags= match_default);
2.7. regex_replace
The algorithm regex_replace searches through a string finding all the matches to the regular expression: for each match it then calls match_results<>::format to format the string and sends the result to the output iterator. Sections of text that do not match are copied to the output unchanged only if the flags parameter does not have the flag format_no_copy set. If the flagformat_first_only is set then only the first occurrence is replaced rather than all occurrences.template <classtraits,classFormatter> basic_string<charT> regex_replace(constbasic_string<charT>& s,Formatter fmt,match_flag_typeflags= match_default);
2.8. regex_iterator
The iterator type regex_iterator will enumerate all of the regular expression matches found in some sequence。typedef regex_iterator<constchar*> cregex_iterator; typedef regex_iterator<std::string::const_iterator> sregex_iterator; #ifndef BOOST_NO_WREGEX typedef regex_iterator<constwchar_t*> wcregex_iterator; typedef regex_iterator<std::wstring::const_iterator> wsregex_iterator; #endif
2.9. regex_token_iterator
When class regex_token_iterator is used to enumerate a single sub-expression with index -1,then the iterator performs field splitting: that is to say it enumerates one character sequence for each section of the character container sequence that does not match the regular expression specified。typedef regex_token_iterator<constchar*> cregex_token_iterator; typedef regex_token_iterator<std::string::const_iterator> sregex_token_iterator; #ifndef BOOST_NO_WREGEX typedef regex_token_iterator<constwchar_t*> wcregex_token_iterator; typedef regex_token_iterator<<std::wstring::const_iterator> wsregex_token_iterator; #endif
2.10. 示例
//g++ demon_regex_boost.cc -o demon_regex_boost -lboost_regex
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <boost/regex.hpp>
using namespace std;
class regex_callback
{
public:
template<typename T>
void operator()(const T& what){
std::cout<<what[0].str()<<std::endl;
}
};
bool regex_callback2(const boost::cmatch& what)
{
std::cout<<what[0].str()<<std::endl;
}
int main(int argc,char **argv)
{
const char *text = " 192.168.0.1 abc 10.0.0.255 10.5.1 1.2.3.4a 5.4.3.2 ";
const char pattern[] = "(\\d)+\\.(\\d)+\\.(\\d)+\\.(\\d)+";
{
//字符串匹配
cout<<"[1]:"<<endl;
boost::regex reg(pattern);
bool ret = boost::regex_match("1.2.3.4",reg);
if(ret){
cout<<"match"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"no match"<<endl;
}
}
{
//提取字串
cout<<"[2]:"<<endl;
boost::smatch sm;
boost::regex reg(pattern);
string text_str(text);
string::const_iterator start = text_str.begin();
string::const_iterator end = text_str.end();
while(boost::regex_search(start,end,sm,reg)){
cout<<sm[0]<<endl;
start = sm[0].second;
}
}
{
//替换
cout<<"[3]:"<<endl;
boost::regex reg(pattern);
string s = boost::regex_replace(string(text),reg,"ftp://$2$5");
cout<<"ftp site:"<<s<<endl;
}
{
//使用迭代器找出所有数字
cout<<"[4]:"<<endl;
boost::regex reg("\\d+");
boost::cregex_iterator it_begin = make_regex_iterator(text,reg);
boost::cregex_iterator it_end;
//for(boost::cregex_iterator it = it_begin ; it != it_end ; ++it){
// cout<<it->str()<<endl;
//}
//for_each(it_begin,it_end,regex_callback());
for_each(it_begin,®ex_callback2);
}
{
cout<<"[5]:"<<endl;
boost::regex ip_regex(pattern);
string text1(text);
boost::sregex_iterator it(text1.begin(),text1.end(),ip_regex);
boost::sregex_iterator end;
for (; it != end; ++it) {
std::cout << it->str() << std::endl;
}
}
}
3. Reference
http://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/Regular-Expressions.html http://see.xidian.edu.cn/cpp/html/1428.html http://www.cppblog.com/tianbianlan/archive/2009/07/24/91015.html http://blog.csdn.net/ghlfllz/article/details/6299846 http://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_54_0/libs/regex/doc/html/index.html版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。