实战:实现一个LRU
Cache
缓存的两个要素: 大小、替换策略
常见替换算法:
- LRU - least recently used,最近最少使用( 淘汰最旧数据)
- LFU- least frequently used,最不经常使用(淘汰频次最少数据)
LRU cache
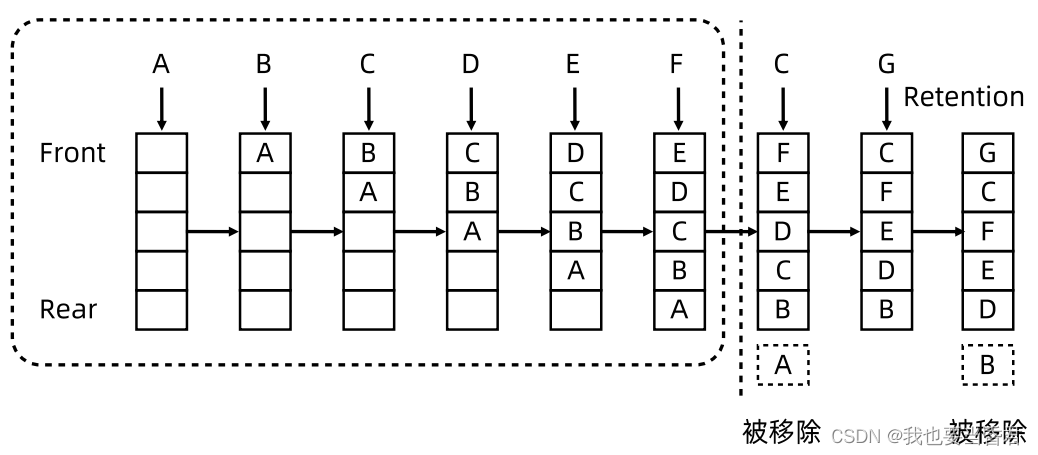
实战:实现一个LRU
146. LRU缓存
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lru-cache/
哈希表+双向链表
- 双向链表用于按时间顺序保存数据
- 哈希表用于把key映射到链表结点(指针/引用)
0(1)访问:直接检查哈希表
0(1)更新:通过哈希表定位到链表结点,删除该结点(若存在) ,在表头重新插入
0(1)删除:总是淘汰链表末尾结点,同时在哈希表中删除
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
this->capacity = capacity;
head = new Node();
tail = new Node();
size = 0;
head->next = tail;
tail->pre = head;
}
int get(int key) {
if(h.find(key) == h.end()){
return -1;
}
Node* node = h[key];
remove(node);
insert(head,node);
return node->value;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if(h.find(key) == h.end()){
Node* node = new Node();
node->key = key;
node->value = value;
h[key] = node;
insert(head,node);
if(h.size() > capacity){
h.erase(tail->pre->key);
remove(tail->pre);
}
}else{
Node* node = h[key];
node->value = value;
remove(node);
insert(head,node);
}
}
private:
struct Node {
int key;
int value;
Node* pre;
Node* next;
};
unordered_map<int,Node*> h;
Node* head;
Node* tail;
int size;
int capacity;
void insert(Node* p,Node* node){
node->next = p->next;
node->pre = p;
p->next->pre = node;
p->next = node;
}
void remove(Node* node){
node->pre->next = node->next;
node->next->pre = node->pre;
}
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class LRUCache
{
unordered_map<int, list<pair<int, int>>::iterator> hash;
list<pair<int, int>> cache;
int size;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) : size(capacity) {}
int get(int key)
{
auto it = hash.find(key);
if (it == hash.end())
{
return -1;
}
cache.splice(cache.begin(), cache, it->second);
return it->second->second;
}
void put(int key, int value)
{
auto it = hash.find(key);
if (it != hash.end())
{
it->second->second = value;
return cache.splice(cache.begin(), cache, it->second);
}
cache.insert(cache.begin(), make_pair(key, value));
hash[key] = cache.begin();
if (cache.size() > size)
{
hash.erase(cache.back().first);
cache.pop_back();
}
}
};
推荐一个零声学院免费公开课程,个人觉得老师讲得不错,分享给大家:Linux,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK等技术内容,立即学习
原文地址:https://www.jb51.cc/wenti/3280846.html
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。




