一、 实验目的
二、实验内容
-
编写函数求两个整数的最大公约数和最小公倍数。
-
编写函数输出指定行数的星星等腰三角形。例如输入:5,得到以下图形。

-
编写函数实现输出从1 开始的整数矩阵。例如输入4,5,则能够输出4x5的矩阵:
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15
16 17 18 19 20 -
编写函数求平面中两个点坐标(x1,y1)与(x2,y2)的距离。例如输入:0 0 3 4,则得到坐标(0,0)与(3,4)两个点之间的距离为5。
-
理解下面的程序,并在IDE中运行,查看结果,回答程序后面的问题。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
int main()
{
int i = 5;
int j = 10;
cout<<"Before swap: i="<<i<<",j="<<j<<endl;
swap(i,j); -------------------------------------------------------①
cout<<"After the first swap: i="<<i<<",j="<<j<<endl;
swap(&i,&j); -----------------------------------------------------②
cout<<"After the second swap: i="<<i<<",j="<<j<<endl;
return 0;
}
问题一:上述程序3的输出结果是什么?
答:
问题二:程序3在①处函数调用后并不能实现两个数的交换,而②处却可以,为什么?
答:
题三:程序3在②处调用的是哪个重载函数?
答
三、实验步骤及结果
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int Factorial(int n){
if(n<0){
cout<<"输入错误!"<<endl;
}else if(n==0){
return 1;
}else{
return n*Factorial(n-1);
}
}
int main (){
int n,f;
cout<<"请输入整数n"<<endl;
cin>>n;
f=Factorial(n);
cout<<n<<"!="<<f<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果
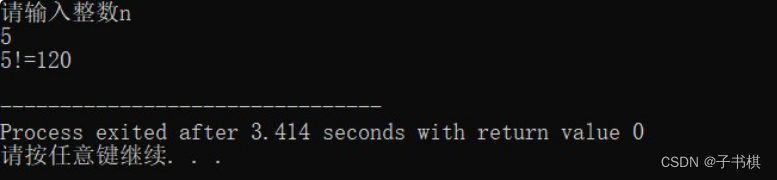
- 编写函数求两个整数的最大公约数和最小公倍数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int Ymax(int x,int y){
int m;
while (y!=0) {
m=x%y;
x=y;
y=m;
}
return x;
}
int Bmin(int x,int y){
int n=x*y;
return n/Ymax(x,y);
}
int main (){
int a, b;
cout<<"请输入两个数:"<<endl;
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<"最大公约数为:"<<Ymax(a,b)<<endl;
cout<<"最小公倍数为:"<<Bmin(a,b)<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果
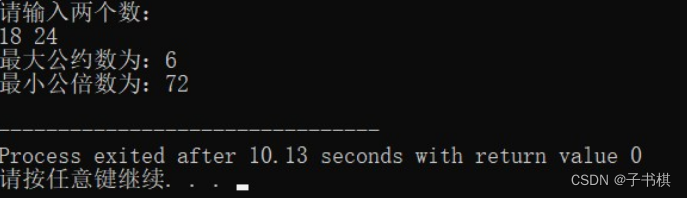
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char show(int n){
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=10;j++)
cout<<" ";
for(int j=1;j<=n-i;j++)
cout<<" ";
for(int j=1;j<=2*i-1;j++)
cout<<"*";
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main (){
int n;
cout<<"请输入图形的行数:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
cout<<endl;
show(n);
return 0;
}
运行结果
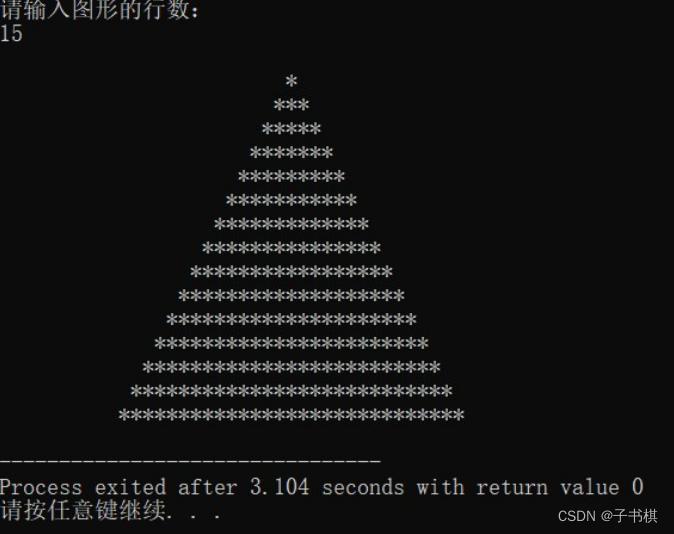
4.编写函数实现从键盘输入一个正整数,将其按照二进制进行输出。例如,将135打印成10000111.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int transfer(int x){
int p=1,y=0,m;
while(1){
m=x%2;
x/=2;
y+=m*p;
p*=10;
if(x<2){
y+=x*p;
break;
}
}
return y;
}
int main(){
int x;
cout<<"请输入一个十进制数:"<<endl;
cin>>x;
cout<<x<<"转换成二进制数是:"<<transfer(x)<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果
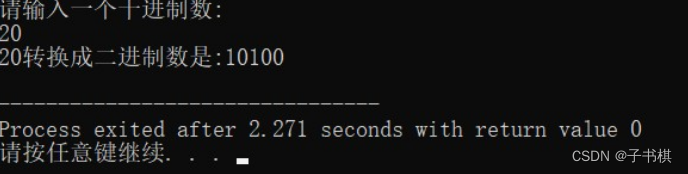
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int gz(int x,int y){
for(int i=1;i<=x;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=y;j++){
cout <<y*(i-1)+j<<"\t";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
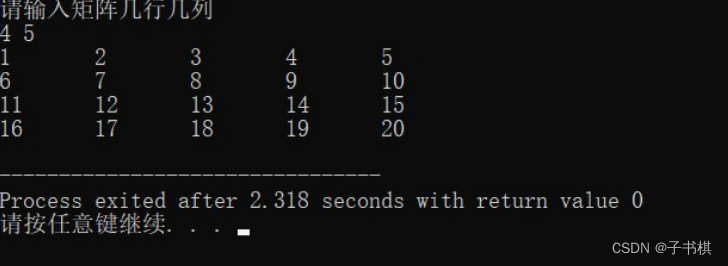
int main (){
int x,y;
cout<<"请输入矩阵几行几列"<<endl;
cin>>x>>y;
gz(x,y);
return 0;
}
运行内容
using namespace std;
int yz(int n){
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(n%i==0)
cout<<i<<"\t";
}
}
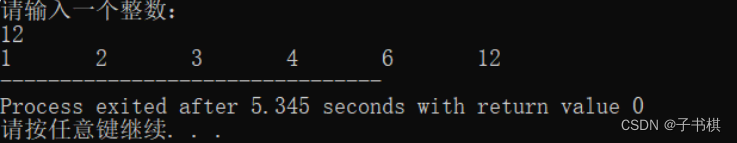
int main (){
int n;
cout<<"请输入一个整数:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
yz(n);
return 0;
}
运行结果
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int zishu(int x,int y){
for(int i=x;i<=y;i++){
int j=0;
for(j=2;j<=i;j++){
if(i%j==0){
break;
}
}
if(i==j){
cout<<i<<"\t";
}
}
}
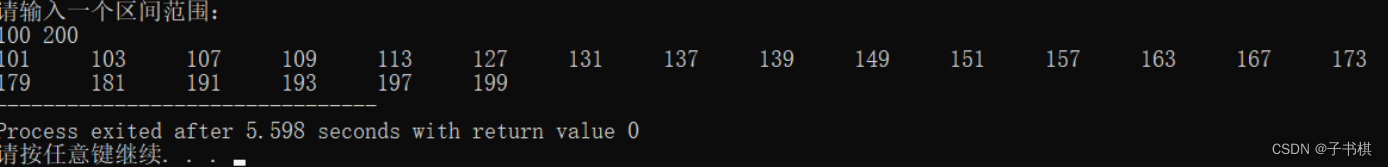
int main (){
int a,b;
cout<<"请输入一个区间范围:"<<endl;
cin>>a>>b;
zishu(a,b);
return 0;
}
运行结果
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
void Long(int x1,int x2,int y1,int y2){
cout<<"两点的距离为:"<<sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2))<<endl;
}
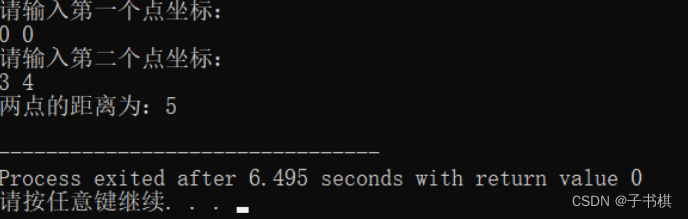
int main(){
int x1,x2,y1,y2;
cout<<"请输入第一个点坐标:"<<endl;
cin>>x1>>y1;
cout<<"请输入第二个点坐标:"<<endl;
cin>>x2>>y2;
Long(x1,x2,y1,y2);
returyn 0;
}
运行结果
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
bool Validate(double a, double b, double c);
void CalAndOutputArea(double a, double b, double c);
void CalAndOutputArea(double w, double h);
void CalAndOutputArea(double r);
int main() {
double a, b, c, w, h, r;
int n;
while(1) {
cout<<"请选择你想计算的类型"<<endl;
cout<<"1-三角形"<<endl;
cout<<"2-矩形"<<endl;
cout<<"3-圆形"<<endl;
cout<<"4-退出"<<endl;
cout<<"请选择命令号1-3:";
cin>>n;
if(n==4) break;
else {
switch(n) {
case 1:
cout<<"请输入三角形的三边长度:";
cin>>a>>b>>c;
if(Validate(a, b, c))
CalAndOutputArea(a,b,c);
else
cout<<"错误:不能构成三角形!"<<endl;
break;
case 2:
cout<<"请输入矩形的两边长:";
cin>>w>>h;
CalAndOutputArea(w, h);
break;
case 3:
cout<<"请输入圆形的半径:";
cin>>r;
CalAndOutputArea(r);
break;
}
cout<<"按Enter键继续……";
cin.get();
cin.get();
system("cls");
}
}
return 0;
}
bool Validate(double a, double b, double c) {
if((a>0) && (b>0) && (c>0)) {
if((a+b)<=c) return 0;
if((a+c)<=b) return 0;
if((c+b)<=a) return 0;
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
void CalAndOutputArea(double a, double b, double c) {
double s = (a+b+c)/2.0;
double area = sqrt(s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c));
cout<<"三角形("<<a<<","<<b<<","<<c<<","<<")的面积是:"<<area<<endl;
}
void CalAndOutputArea(double w, double h) {
double area = w * h;
cout<<"矩形("<<w<<","<<h<<")的面积是:"<<area<<endl;
}
void CalAndOutputArea(double r) {
const double PI = 3.1415926;
double area = PI*r*r;
cout<<"圆形(半径r:"<<r<<")的面积是:"<<area<<endl;
}
运行结果
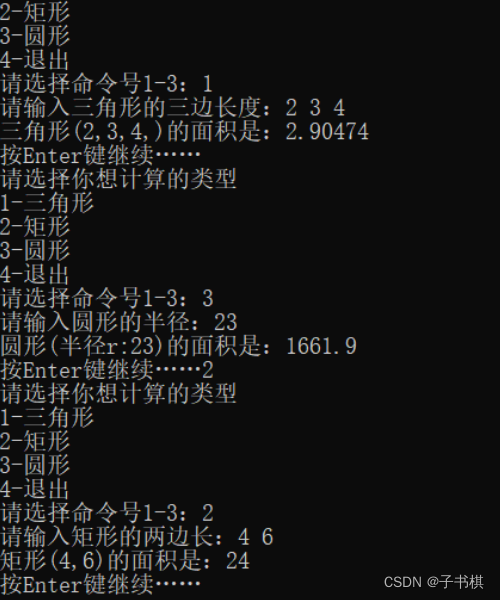
10.理解下面的程序,并在IDE中运行,查看结果,回答程序后面的问题。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
int main()
{
int i = 5;
int j = 10;
cout<<"Before swap: i="<<i<<",j="<<j<<endl;
swap(i,j); -------------------------------------------------------①
cout<<"After the first swap: i="<<i<<",j="<<j<<endl;
swap(&i,&j); -----------------------------------------------------②
cout<<"After the second swap: i="<<i<<",j="<<j<<endl;
return 0;
}
问题一:上述程序3的输出结果是什么?
答:
Before swap: i=5,j=10
After the first swap: i=5,j=10
After the second swap: i=10,j=5
问题二:程序3在①处函数调用后并不能实现两个数的交换,而②处却可以,为什么?
答:①处函数调用实质上是值传递给形参,不会改变实参。而②处调用的是引用函数,相当于给实参改变了一个名字在函数里进行操作,会改变实参。
答:第二个void swap(int *a, int *b)
四、实验小结
问题与解决办法:
1.
编译出错 :[Error] ‘sqrt’ was not declared in this scope
解决办法:运用sqrt函数需要头文件#include <math.h>。
2.
编译出错,提示“[Error] expected before return”
解决办法:语句结束时的英文下的分号“;”输成了中文下的分号。改正后,错误消失。
3.
编译出错,提示“ [Error] expected ‘;’ before ‘)’ token”
解决办法:for循环里的分号“;”写成了逗号“,”。改正后,错误消失。
若对您有帮助,请关注点赞,后续持续更新!!
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。





