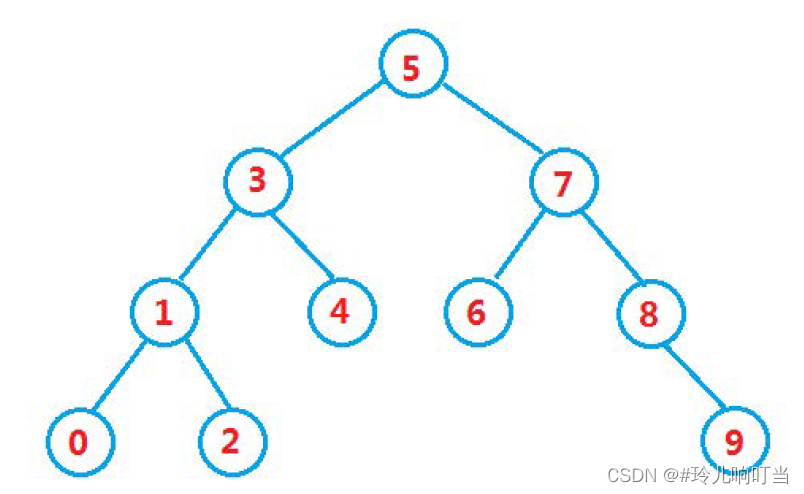
一、二叉搜索树
1.1概念
-
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
public class BinarySearchTree {
class TreeNode{
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val){
this.val=val;
}
}
public TreeNode root;
//1 查找key是否存在于二叉搜索树中
//用cur遍历查找
public TreeNode search(int key){
TreeNode cur=root;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<key){
cur=cur.left;
}else if(cur.val>key){
cur=cur.right;
}else{
return cur;
}
}
return null;
}
//2插入结点
//树的节点之间也是有关联的,要插入新的结点的话,只能插入到现有结点的left或者right
public boolean insert(int key){
TreeNode node=new TreeNode(key);
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode parent=null;
if(cur==null){
root=node;
}
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val>key){
parent=cur;
cur=cur.left;
}else if(cur.val<key){
parent=cur;
cur=cur.right;
}else{
return false;//存在相同的元素,不能插入成功
}
}
if(parent.val>key){
parent.left=node;
}
if(parent.val<key){
parent.right=node;
}
return true;
}
//3 删除关键字为key 的结点
public void remove(int key){
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode parent=null;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val>key){
parent=cur;
cur=cur.left;
}else if(cur.val<key){
parent=cur;
cur=cur.right;
}else{
removeNode(cur,parent);
return;
}
}
}
private void removeNode(TreeNode cur,TreeNode parent){
if(cur.left==null){
if(cur==root){
cur=cur.right;
}else if(cur==parent.left){
parent.left=cur.right;
}else{
parent.right=cur.right;
}
}else if(cur.right==null){
if(cur==root){
cur=cur.left;
}else if(cur==parent.left){
parent.left=cur.left;
}else{
parent.right=cur.left;
}
}else{
TreeNode targetParent=cur;
TreeNode target=cur.right;
while(cur.left!=null){
targetParent=target;
target=target.left;
}
cur.val=target.val;
if(targetParent.left==target){
targetParent.left=target.right;
}else{
targetParent.right=target.right;
}
}
}
}
二、Map和Set
2.1 概念
Map和set是一种专门用来进行搜索的容器或者数据结构,其搜索的效率与其具体的实例化子类有关。以前常见的搜索方式有:
- 直接遍历,时间复杂度为O(N),元素如果比较多效率会非常慢
- 二分查找,时间复杂度为,但搜索前必须要求序列是有序的
上述排序比较适合静态类型的查找,即一般不会对区间进行插入和删除操作了,而现实中的查找比如:
可能在查找时进行一些插入和删除的操作,即动态查找,那上述两种方式就不太适合了,Map和Set是一种适合动态查找的集合容器。
2.2 模型
一般把搜索的数据称为关键字(Key),和关键字对应的称为值(Value),将其称之为Key-value的键值对,所以模型会有两种:
- 纯 key 模型,比如:
有一个英文词典,快速查找一个单词是否在词典中快速查找某个名字在不在通讯录中 - Key-Value 模型,比如:
统计文件中每个单词出现的次数,统计结果是每个单词都有与其对应的次数:<单词,单词出现的次数>
而Map中存储的就是key-value的键值对,Set中只存储了Key。
三、Map的使用
3.1 Map接口说明
- Map是一个接口,不能直接实例化对象,如果要实例化对象只能实例化其实现类TreeMap或者HashMap
- Map中存放键值对的Key是唯一的,value是可以重复的
- Map中的Key可以全部分离出来,存储到Set中来进行访问(因为Key不能重复)。
- Map中的value可以全部分离出来,存储在Collection的任何一个子集合中(value可能有重复)。
- Map中键值对的Key不能直接修改,value可以修改,如果要修改key,只能先将该key删除掉,然后再来进行重新插入。
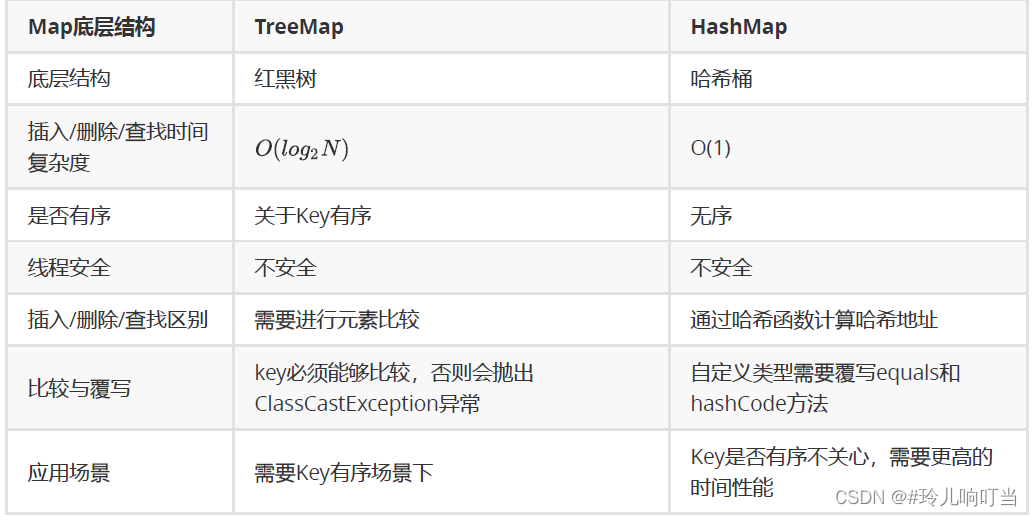
- TreeMap和HashMap的区别
3.2 Map的常用方法说明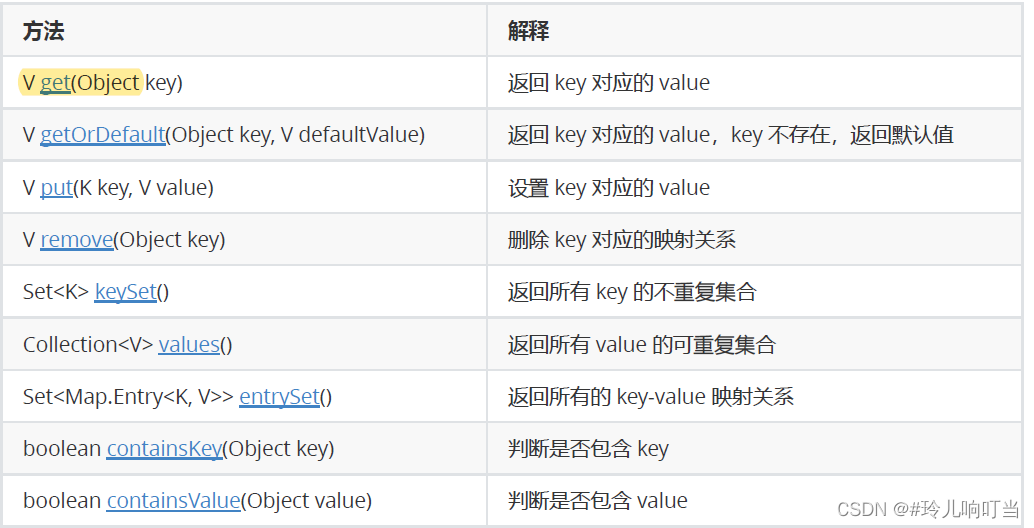
public class Test {
public static void main1(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map1=new TreeMap<>();
Map<String,Integer> map2=new HashMap<>();
Set<String> set1=new TreeSet<>();
Set<String> set2=new HashSet<>();
}
public static void main2(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map=new TreeMap<>();
map.put("abc",10);
map.put("hello",3);
map.put("hello2",8);
map.put(null,1);
System.out.println(map.get("hello"));
System.out.println(map.getorDefault("hello",100));
System.out.println("=====================================");
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet=map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:entrySet){
System.out.println("key:"+entry.getKey()+"val:"+entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println("=====================================");
Collection<Integer> list=map.values();
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("====================================");
Set<String> set=map.keySet();
System.out.println(set);
System.out.println("=====================================");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set=new TreeSet<>();
set.add("abc");//去重
System.out.println(set);
}
}
四、Set的说明
- Set与Map主要的不同有两点:Set是继承自Collection的接口类,Set中只存储了Key。
4.1 常见方法说明
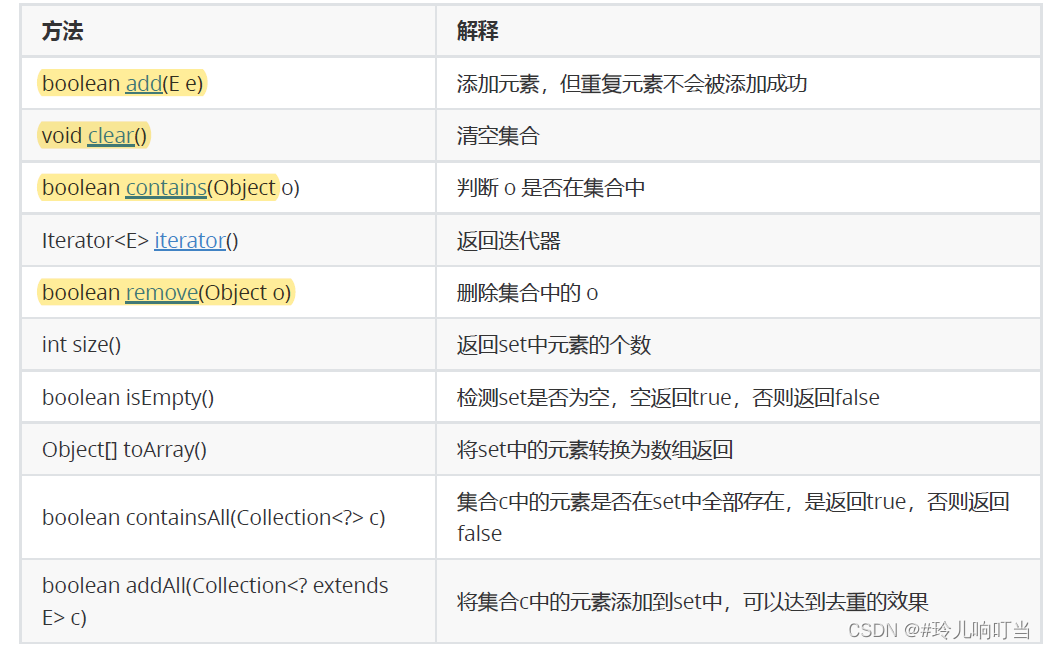
- Set是继承自Collection的一个接口类
- Set中只存储了key,并且要求key一定要唯一
- Set的底层是使用Map来实现的,其使用key与Object的一个默认对象作为键值对插入到Map中的
- Set最大的功能就是对集合中的元素进行去重
- 实现Set接口的常用类有TreeSet和HashSet,还有一个LinkedHashSet,LinkedHashSet是在HashSet的基础
上维护了一个双向链表来记录元素的插入次序。 - Set中的Key不能修改,如果要修改,先将原来的删除掉,然后再重新插入
- Set中不能插入null的key。
- TreeSet和HashSet的区别
原文地址:https://www.jb51.cc/wenti/3285134.html
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。




