目录
一.栈
栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。

栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
//静态栈的结构
typedef int STDataType;
#define N 10
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType _a[N];
int _top; // 栈顶
}Stack;
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;实际中一般静态栈不实用,所以我们主要实现支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* arr;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
void StackDestory(Stack* ps);
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType x);
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackDestory(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->arr);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//压栈
ps->arr[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
return ps->top;
}
二.队列
队列的概念及结构
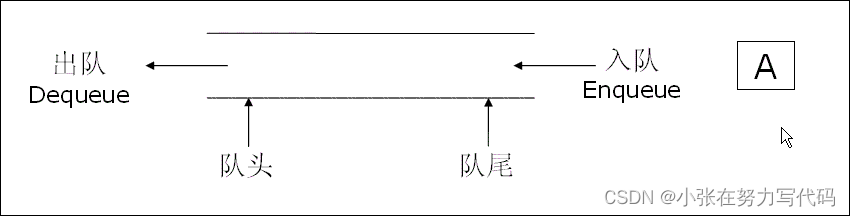
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。所以下面我们用链式结构实现队列。
typedef int QDaTaType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDaTaType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDaTaType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDaTaType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDaTaType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* del = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(del);
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDaTaType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->head == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->head->next == NULL)//队列中剩下最后一个节点时
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* del = pq->head;
pq->head = pq->head->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDaTaType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
QDaTaType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL && pq->tail == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
三.栈和队列面试题
1.括号匹配问题
题目链接
题目描述
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
1.左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
2.左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。示例 1:
输入:s = "()"
输出:true
示例 2:输入:s = "()[]{}"
输出:true
示例 3:输入:s = "(]"
输出:false
示例 4:输入:s = "([)]"
输出:false
示例 5:输入:s = "{[]}"
输出:true提示:s仅由括号
'()[]{}'组成
解题思路
创建一个栈,遍历字符串s,遇到左括号就入栈,遇到右括号就pop栈顶元素,与右括号比较,如果不符合就return false,如果栈已经为空,也return false,直到s被遍历完毕,然后判断栈是否为空,也就是判断左括号是否完全被成功匹配,如果栈为空,就return true,否则return false。
代码实现
由于C语言没有内置数据结构的库,因此我们需要自己写一个栈。代码如下
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* arr;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
void StackDestory(Stack* ps);
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType x);
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
void StackInit(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackDestory(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->arr);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//压栈
ps->arr[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
return ps->top;
}bool isValid(char * s){
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
while(*s)
{
if(*s == '{' || *s == '[' || *s == '(')
{
StackPush(&st, *s);
}
else
{
if(StackEmpty(&st))
return false;
char top = StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
if ((*s == '}' && top != '{')
|| (*s == ']' && top != '[')
|| (*s == ')' && top != '('))
{
return false;
}
}
++s;
}
bool flag = StackEmpty(&st);
StackDestory(&st);
return flag;
}2.用队列实现栈
题目链接
题目描述
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。注意:
- 你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
示例:
输入:
["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]解释:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
解题思路
代码实现
3.用栈实现队列
题目链接
题目描述
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
- 你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
示例 :
输入:
["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
解题思路
代码实现
4.设计循环队列
题目链接
题目描述
设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
你的实现应该支持如下操作:
MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。
Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。
enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。
deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。
isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。
isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。
示例:
MyCircularQueue circularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3); // 设置长度为 3
circularQueue.enQueue(1); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(2); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(3); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 false,队列已满
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 3
circularQueue.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.deQueue(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 true
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 4
解题思路
代码实现
原文地址:https://www.jb51.cc/wenti/3288386.html
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。




