本文来聊一下在spring中,当spring 容器启动后,我们有几种初始化操作的方式。
文章目录
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class PersonConfig {
@Bean
public Person person(){
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("张三");
person.setAge(18);
return person;
}
}
一、ContextRefreshedEvent事件
ContextRefreshedEvent:是spring容器初始化完成后调用的事件。
ContextRefreshedEvent的父类是ApplicationContextEvent,是一个事件。所以我们通过ApplicationListener来实现。
代码如下:
import com.example.springbootdemo.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class PersonAfterListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
person.run("ContextRefreshedEvent");
}
}
输出结果:
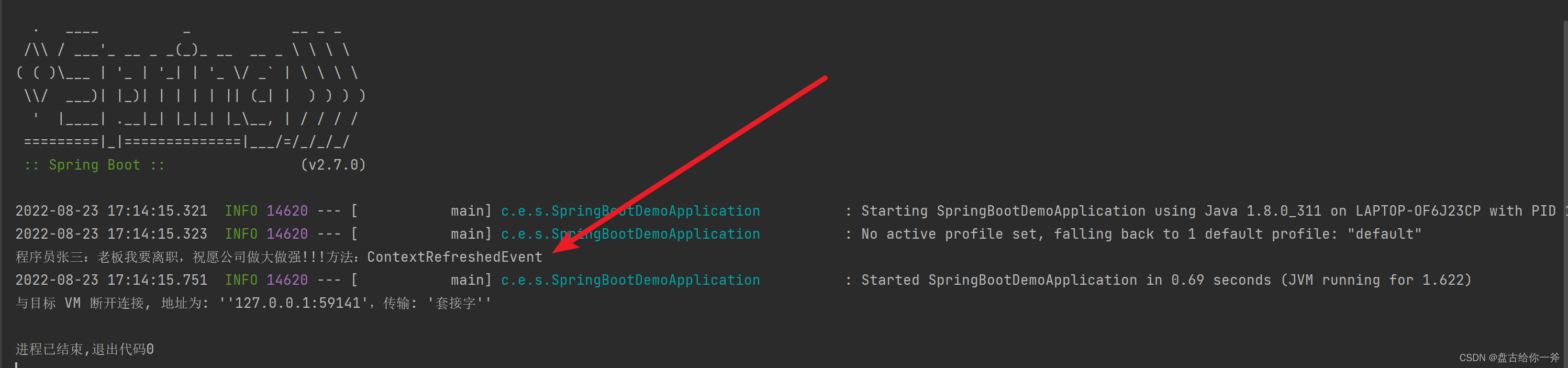
二、postconstruct 注解
postconstruct注解修饰的方式,是在spring容器启动时运行的。优先级大于ContextRefreshedEvent事件。
代码如下:
import com.example.springbootdemo.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.postconstruct;
@Component
public class PersonAfterpostconstruct {
@Autowired
private Person person;
@postconstruct
public void postconstruct(){
person.run("postconstruct");
}
}
输出结果:
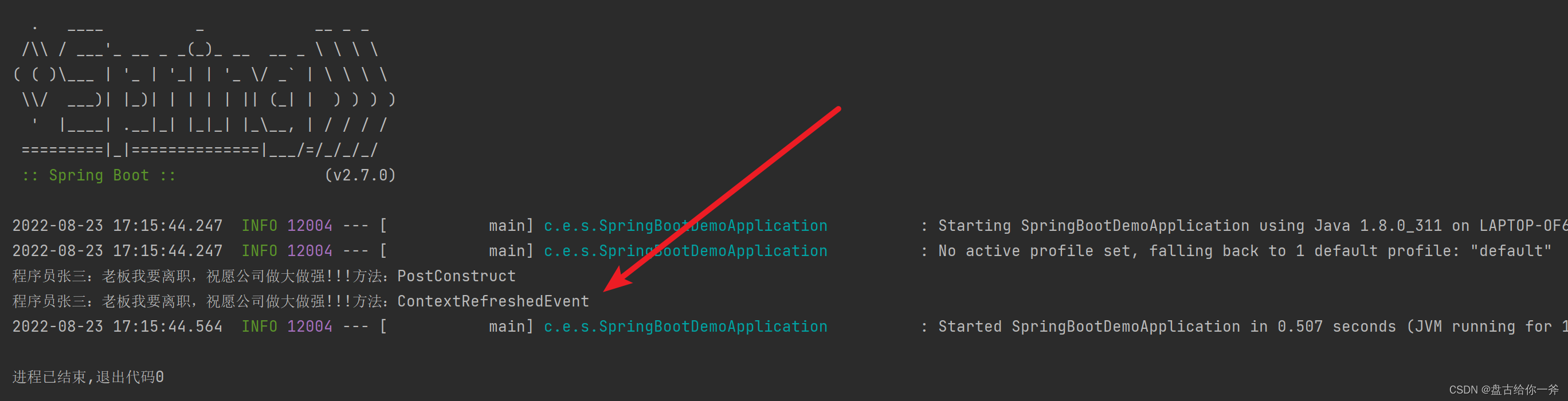
由此可见,postconstruct优先级大于ContextRefreshedEvent事件。
三、InitializingBean
InitializingBean是spring容器在启动并初始化好内部示例后调用的,用来最终为总体bean添加最后属性和操作。
官方原话:This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
代码如下:
import com.example.springbootdemo.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class PersonAfterInitializingBean implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
person.run("InitializingBean");
}
}
输出结果:
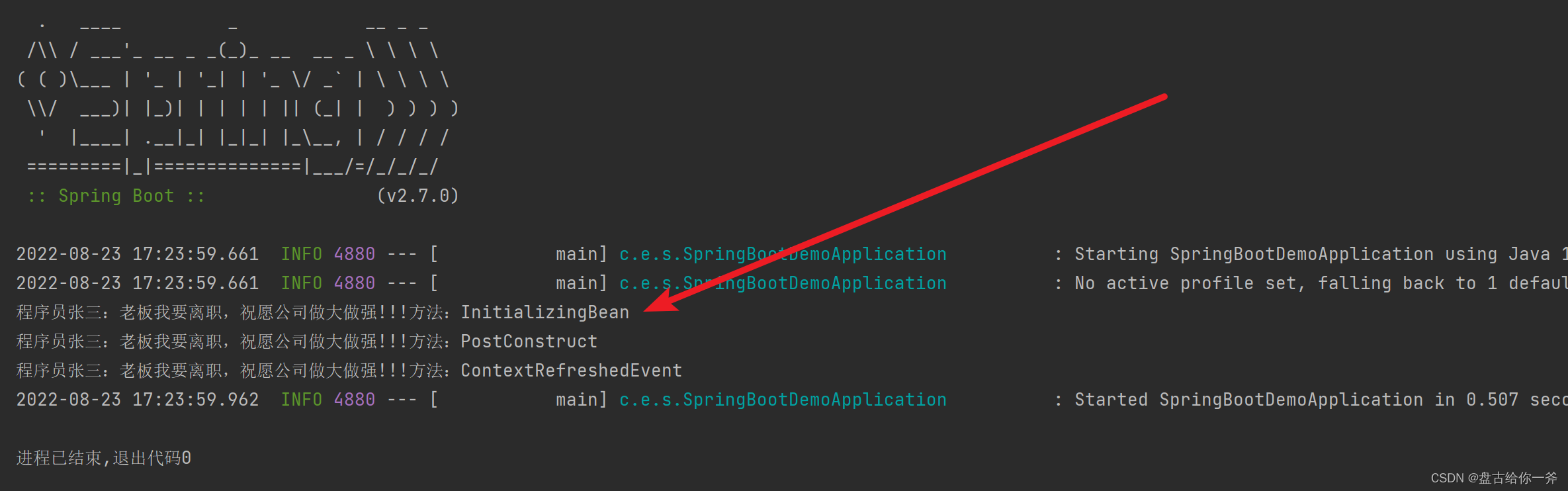
四、init-method方法
这种方法有一定的局限性,并且可能会覆盖曾经的init操作,需要慎用。
Bean在加载到spring容器中时需要先将Bean的定义信息抽象为BeanDeFinition,其中有一个属性init-method代表将来Bean初始化时要调用的方法。
我们通过beanfactoryPostProcessor来注入init-method方法,并且该方法必须是没有参数的。
代码如下:
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDeFinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.beanfactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListablebeanfactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class PersonAfterInit implements beanfactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessbeanfactory(ConfigurableListablebeanfactory beanfactory) throws BeansException {
BeanDeFinition person = beanfactory.getBeanDeFinition("person");
person.setinitMethodName("run");
}
}
输出结果:
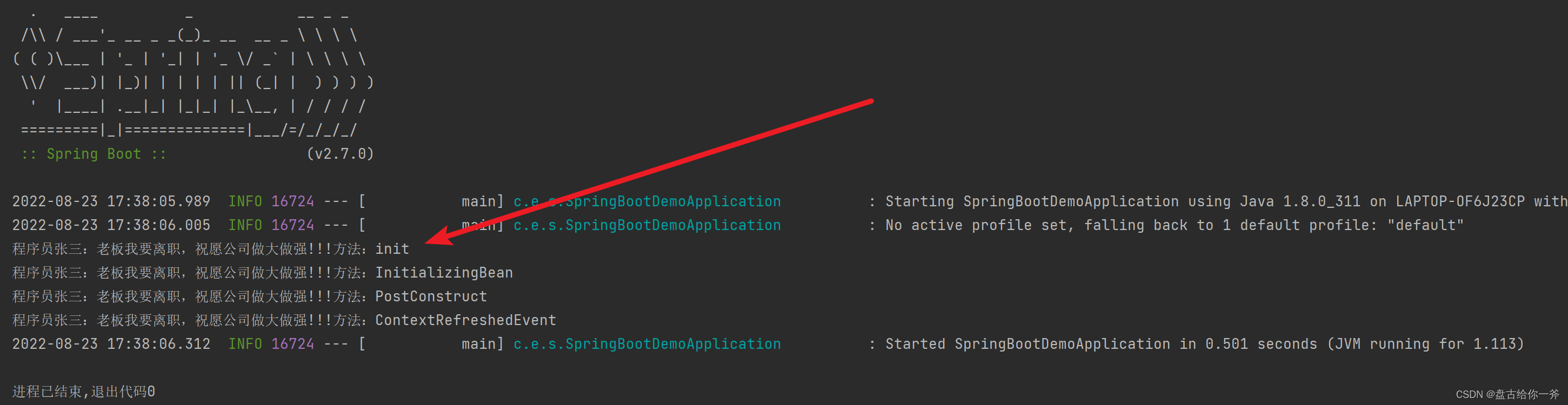
五 、实现 SmartinitializingSingleton 接口
SmartinitializingSingleton是Bean容器在初始化所有非懒加载的单例Bean后调用的方法。
代码如下:
import com.example.springbootdemo.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.SmartinitializingSingleton;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class PersonAfterSmartinitializingSingleton implements SmartinitializingSingleton {
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
person.run("SmartinitializingSingleton");
}
}
输出结果:
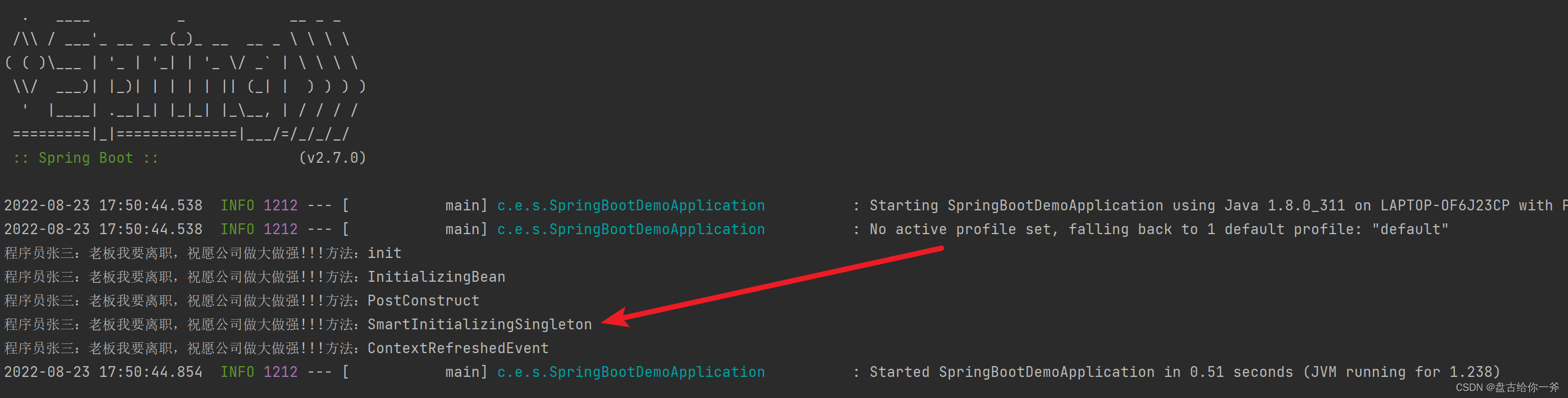
六、重写 onRefresh()方法
这个我实在是不会,但我不藏着掖着,告诉你也能实现。
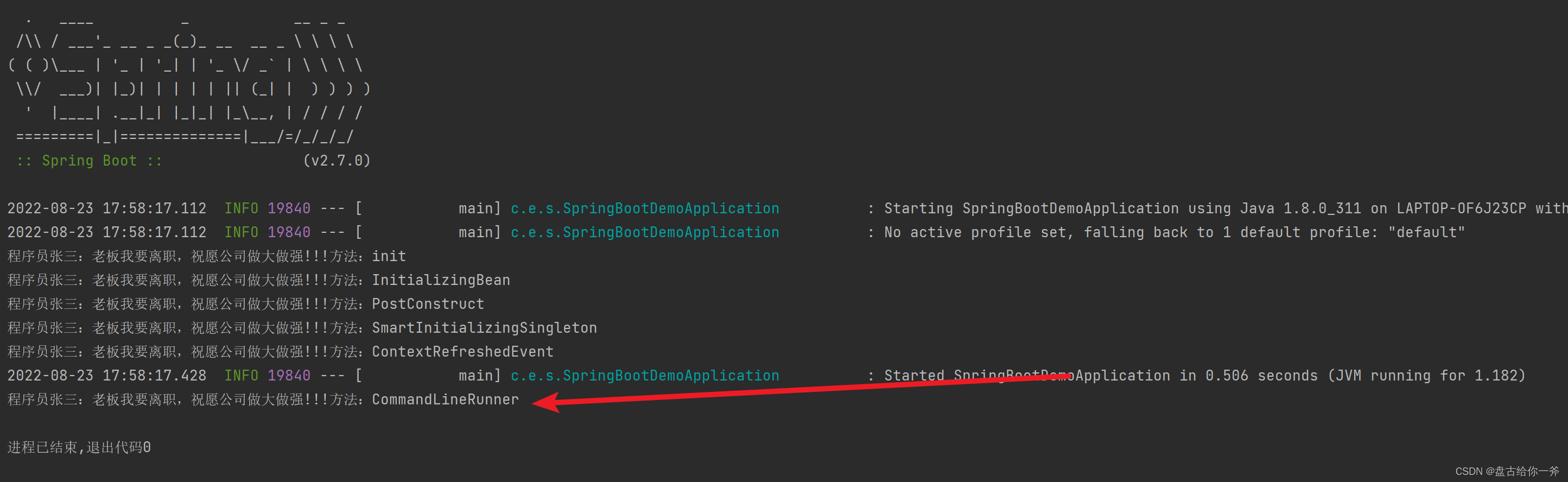
七、CommandLineRunner(仅限Spring Boot)
CommandLineRunner 是一个Spring boot 接口,在应用初始化后执行,且仅会执行一次。可以用来打印项目中配置文件的参数,方便排查问题。
代码如下:
import com.example.springbootdemo.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class PersonAfterCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
person.run("CommandLineRunner");
}
}
输出结果:
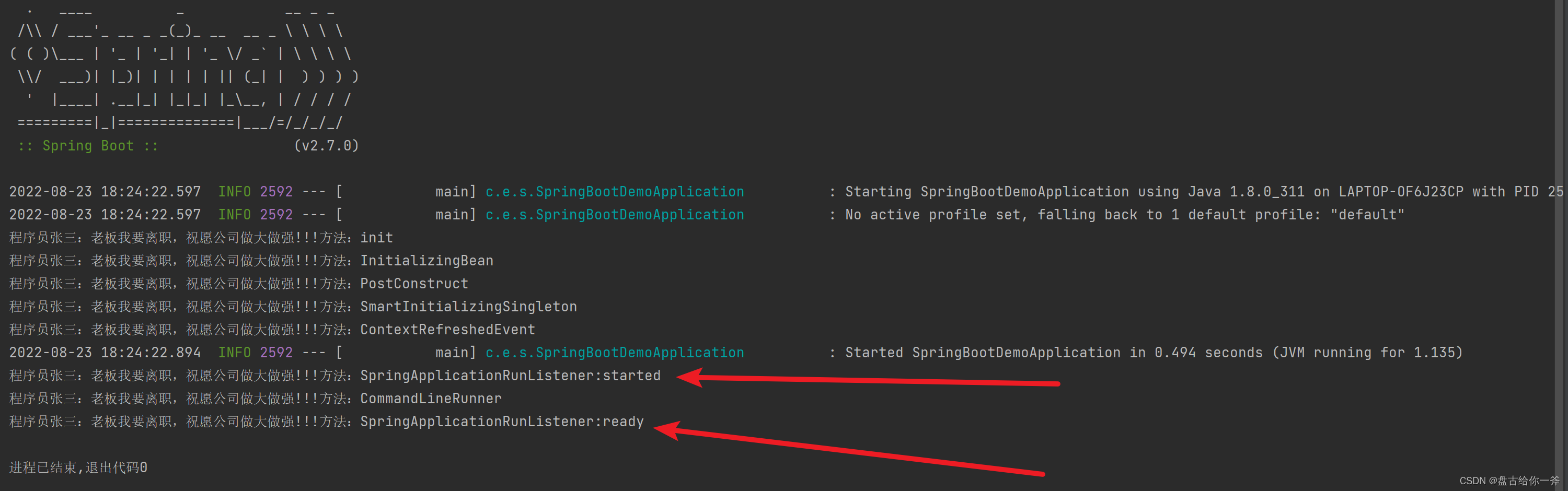
八、SpringApplicationRunListener(仅限Spring boot)
SpringBoot的生命周期事件监听方法,需要搭配resource/meta-inf/spring.factories 文件使用。
代码如下:
JAVA代码:
import com.example.springbootdemo.bean.Person;
import org.springframework.boot.ConfigurableBootstrapContext;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import java.time.Duration;
public class PersonAfterSpringApplicationRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener {
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
public PersonAfterSpringApplicationRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
}
@Override
public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
/*
* Person has not been registered
*/
// Person person = bootstrapContext.get(Person.class);
// person.run("SpringApplicationRunListener:starting");
}
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
/*
* Person has not been registered
*/
// Person person = bootstrapContext.get(Person.class);
// person.run("SpringApplicationRunListener:environmentPrepared");
}
@Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
/*
* Person has not been registered
*/
// Person person = context.getBean(Person.class);
// person.run("SpringApplicationRunListener:contextPrepared");
}
@Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
/*
* Person has not been registered
*/
// Person person = context.getBean(Person.class);
// person.run("SpringApplicationRunListener:contextLoaded");
}
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration tiMetaken) {
Person person = context.getBean(Person.class);
person.run("SpringApplicationRunListener:started");
}
@Override
public void ready(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration tiMetaken) {
Person person = context.getBean(Person.class);
person.run("SpringApplicationRunListener:ready");
}
@Override
public void Failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
Person person = context.getBean(Person.class);
person.run("SpringApplicationRunListener:Failed");
}
}
spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=com.example.springbootdemo.impl.PersonAfterSpringApplicationRunListener
输出结果:
总结:
执行优先级:init-Method >> InitializingBean >> postconstruct >> SmartinitializingSingleton >> ContextRefreshedEvent >> SpringApplicationRunListener:started >> CommandLineRunner >> SpringApplicationRunListener:ready
原文地址:https://www.jb51.cc/wenti/3288707.html
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点与技术仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 dio@foxmail.com 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。




